Wall thickness calculation, as covered in ASME B31.4 Article 402 and ASME B31.8, is initially derived from hoop stress considerations based on design factors. The thickness should be such that the longitudinal shear and equivalent stresses in the pipe wall under functional and environmental loads do not exceed certain values.
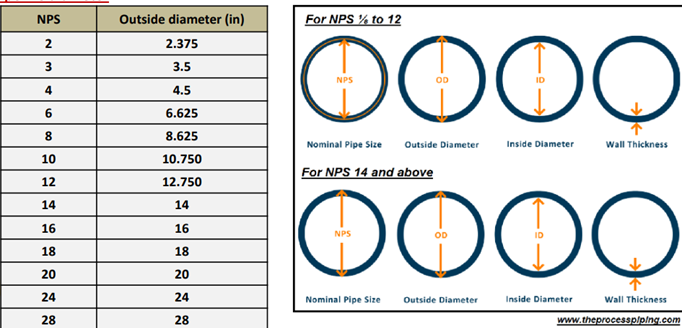
To do the calculation we need the following parameters:
| Input Parameters | Source |
| Design Pressure (MPa) | PEFS |
| Max. and Min. Operating temperature (°C) | PEFS |
| SMYS (MPa) | Below |
| Location class | Below |
| Design factor | Below |
| Corrosion allowance (mm) | PEFS |
| Installation temperature (°C) | Differs from a country to another |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | Below |
| Longitudinal joint factor | Below |
| Temperature de-rating factor (If applicable) | Below |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (m/m °C) | Below |
| Poisson’s ratio | Below |
| Pipeline MAIP (MPa) | PEFS |
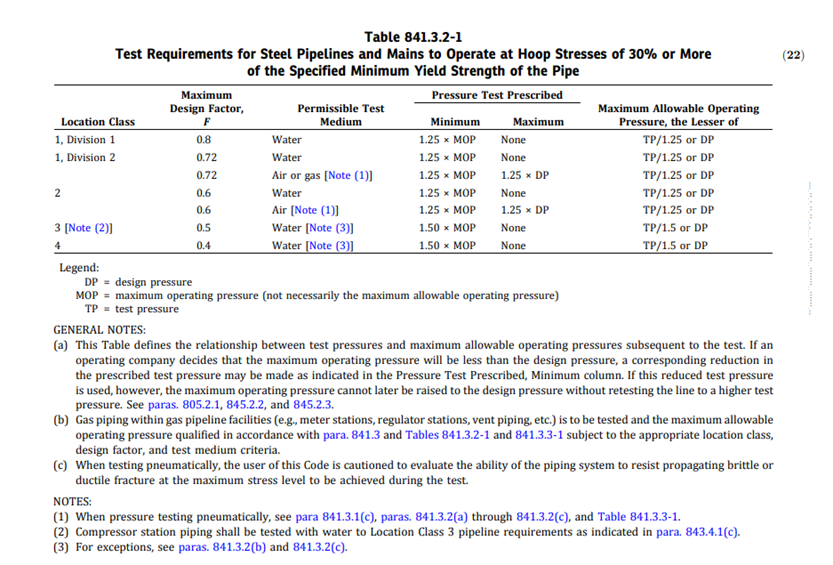
For design factor, we use the following table:
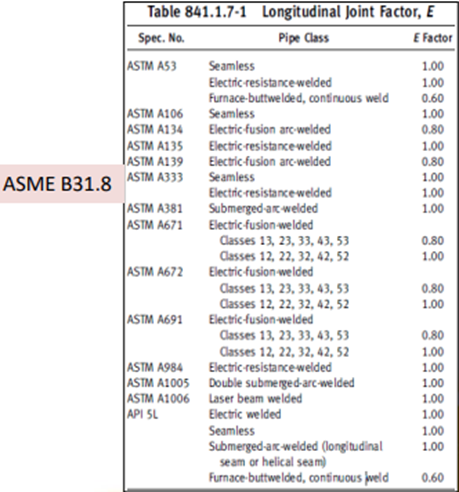
or longitudinal Weld Joint Factor, we use the following table:
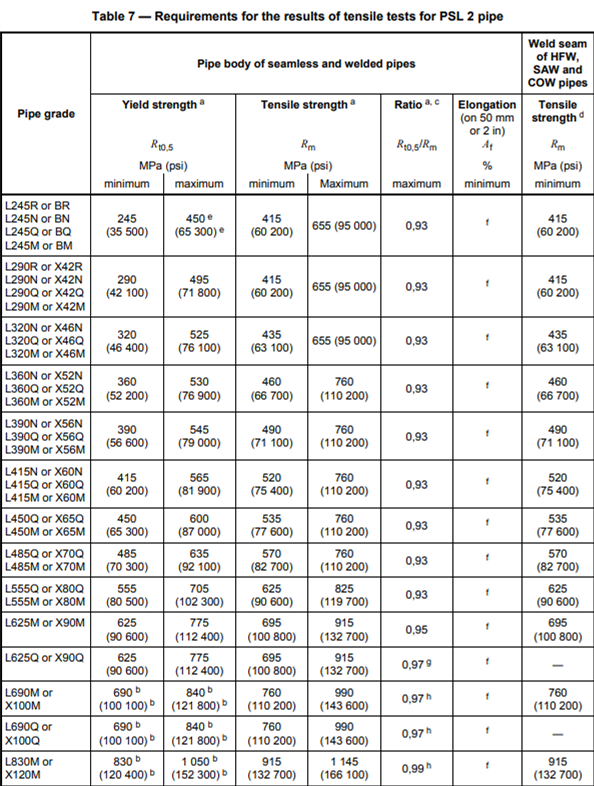
For the SMYS, we use the following table where we take the minimum yield strength:
For modulus of Elasticity, we use the following:
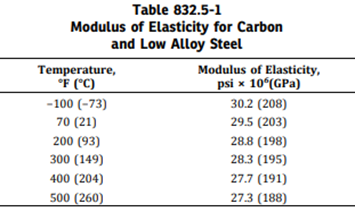
For temperature de-rating factor, we use the following:
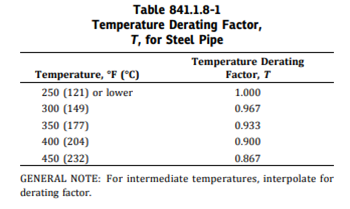
or coefficient of thermal expansion, we use the following:
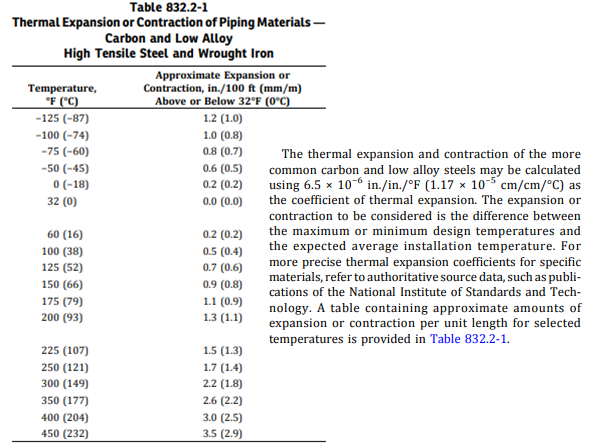
For location class, we use the following:
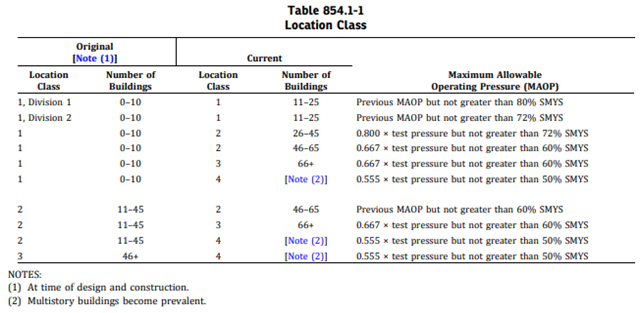
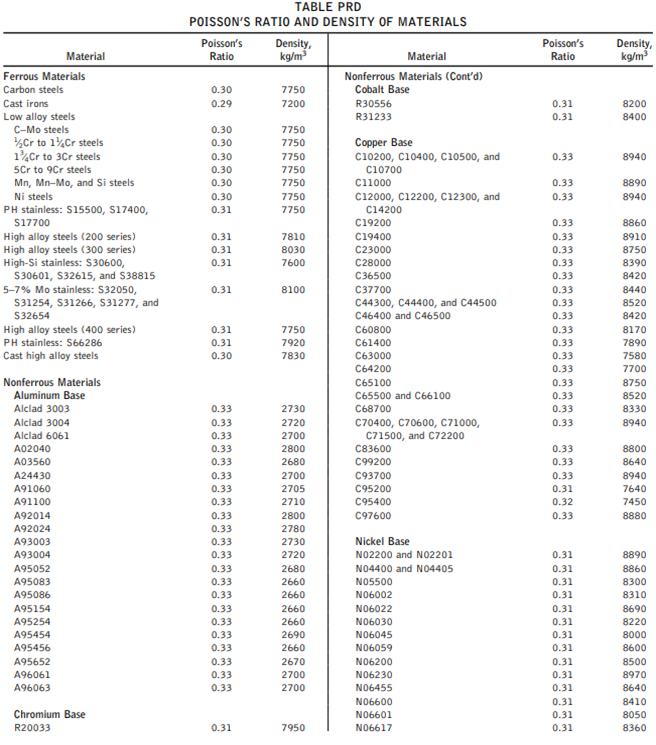
For poison’s ratio, we use the following:
Calculation Method
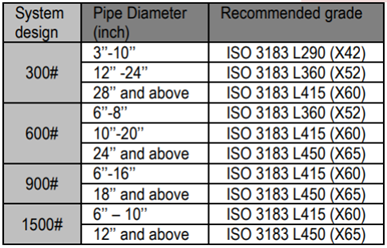
| STEP 1: Select a Material Grade for SMYS |
We select a steel grade based on the following table:
| STEP 2: Calculate the Wall thickness |
We use the following formula:
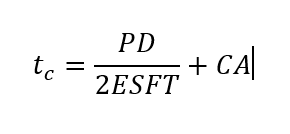
| STEP 3: Check Bend Thinning |
For the value of R, we use the following guidelines:


| STEP 4: Calculate the Stresses (for buried pipelines) |

| STEP 4: Calculate the Stresses & Bending (for aboveground pipelines) |

| STEP 5: Check the MAIP |
Maximum Allowable Incidental Pressure (MAIP): The maximum pressure that is allowed to occur in a pipeline with a limited frequency and duration, determined in accordance with applicable design standard.





