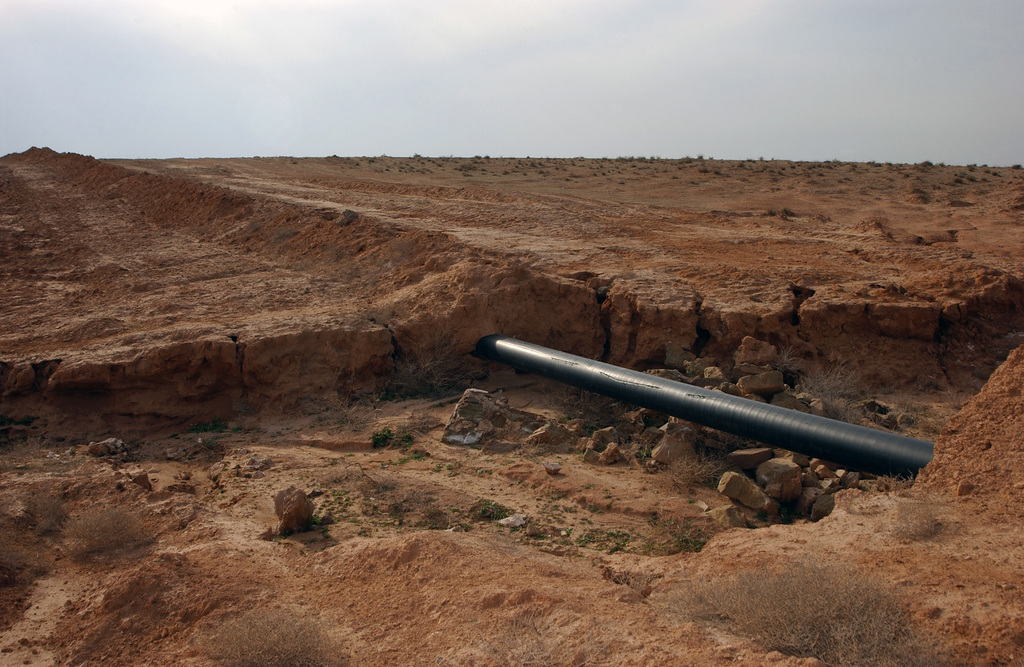
Corrosion protection is a critical aspect of maintaining the integrity of pipelines. Without proper protection, pipelines can degrade over time due to environmental factors, leading to leaks, ruptures, and other catastrophic failures. By applying a protective coating, the lifespan of the pipelines can be significantly extended, ensuring the safe and efficient transport of petroleum and natural gas.
The ISO 21809-1:2018 standard focuses on polyolefin coatings, specifically three-layer polyethylene (PE) and three-layer polypropylene (PP) coatings. Polyolefin is a type of polymer produced from a simple olefin as a monomer. Polyethylene and polypropylene are types of polyolefins. These materials are chosen for their excellent chemical resistance, durability, and versatility.
The coating system shall consist of three layers:
- 1st layer: Epoxy
- 2nd layer: Adhesive
- 3rd layer: PE/PP top layer
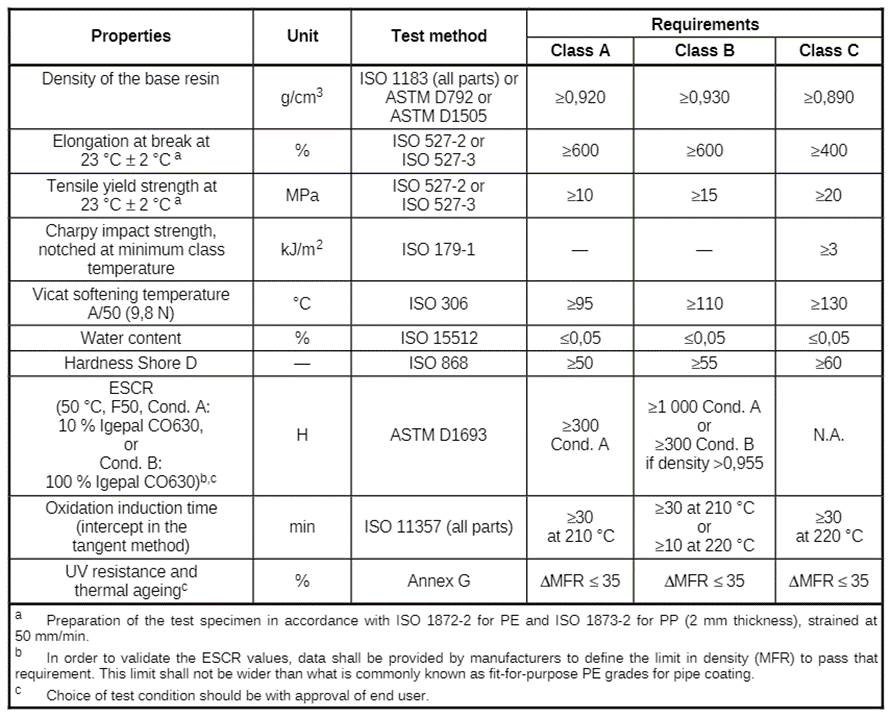
The coating class shall be selected based on the design temperature range and expected field duty. It shall be able to withstand the temperature range required as per the below table as per ISO 21809-1.
| Coating Class | A | B | C |
| Top layer material | LDPE | MDPE/HDPE | PP |
| Design temperature ranges (C) | -20 to 60 | -40 to 80 | -20 to 110 |
PE –> 40 to 80 deg C
PP –> 20 to 130 deg C
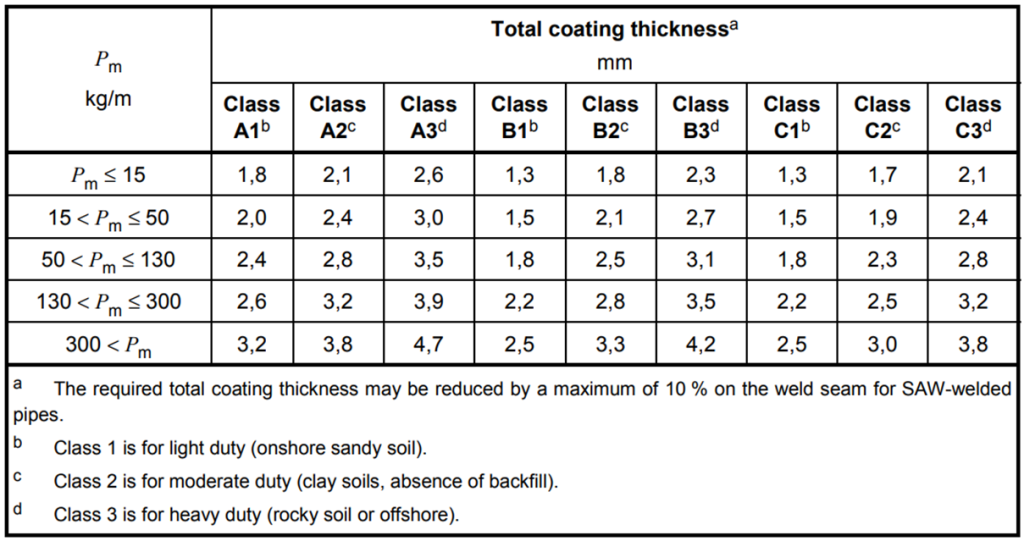
Total Coating Thickness based on coating classes:
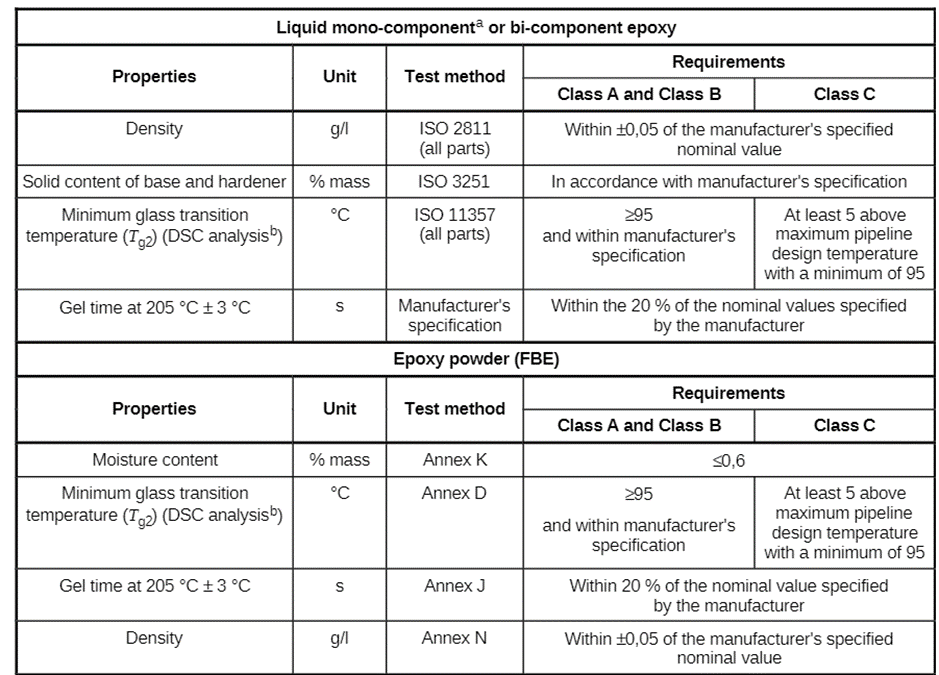
1st layer requirements (Epoxy) in accordance with ISO 21809-1:
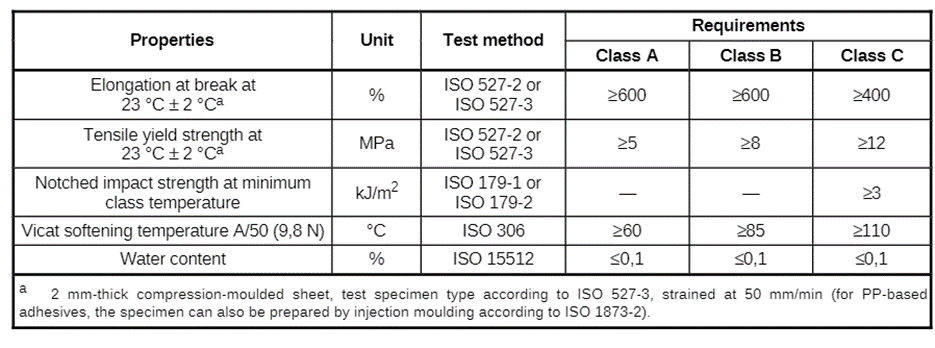
2nd layer requirements (Adhesive) in accordance with ISO 21809-1:
3rd layer requirements (PE/PP top layer) in accordance with ISO 21809-1: