Isolation joints, also known as insulating joints, are integral components of pipeline systems, providing an electrical break between pipeline sections or between pipeline sections and neighboring structures. They are designed to limit the possibility of electrical bridging across the joint, thereby preventing detrimental electro-chemical interaction and improving the effectiveness of the cathodic protection system.
A specific type of isolation joint, the Monolithic Isolation Joint (MIJ), is a single-piece electrical isolation block that is widely used in pipeline systems to reduce corrosion through cathodic protection methods. The MIJ is an integral part of the pipeline system and provides satisfactory long-term integrity. All components of the MIJ system are fully encased in forged steel bodies.
Functional Requirements of Isolation Joints
Isolation joints must be suitable for pigging operations and must withstand the operating conditions stated in the requisition sheets. If the operating conditions are not stated, the following conditions apply: the design temperature should be a maximum of 82 degrees Celsius and a minimum of 5 degrees Celsius. Furthermore, pipeline isolation joints are typically installed in the aboveground part immediately after the aboveground-belowground transition.
Advantages of Monolithic Isolation Joints
For buried pipeline applications, monolithic isolation joints are more common. Their robust steel body prevents external attacks from extreme environments and tampering. In general, MIJs are installed aboveground in pipeline systems to limit the possibility of electrical bridging across the joint. They are intended to be girth welded between two pipeline sections.
The benefits of a monolithic isolation joint include:
- Elimination of the source of a short circuit by removing bolts, sleeves, and washers.
- No requirement for field assembly as there are no flanges, gaskets, nuts, washers, sleeves, or bolts.
- Reduction in the chances of leakage due to improper field assembly.
- Typically, less expensive compared to insulated gasket flange assembly.
Components of Isolation Joints
An isolation joint consists of two spools, each comprising a pipe segment with a beveled end for welding to the pipeline on one side, and a welded-on boltless flange at the other end for encapsulation into isolating and filler material. The material used for the pipe segments should be compatible with the pipeline material. A rigid casting (retaining ring) is used for strength connection.
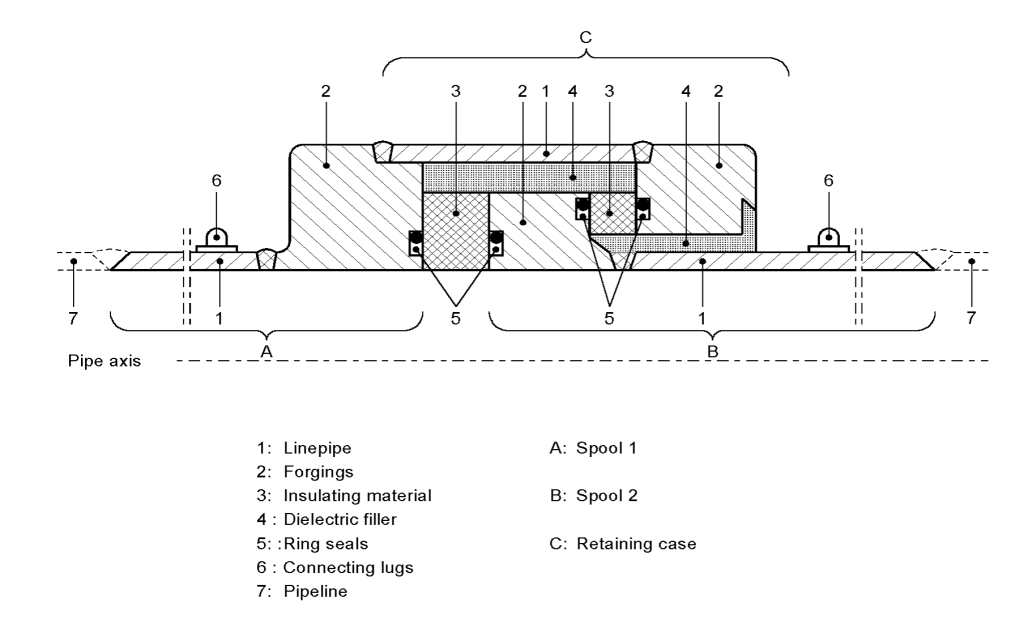
Isolation joints play a crucial role in pipeline systems, providing electrical isolation that enhances the effectiveness of cathodic protection systems and prevents electro-chemical interactions. Their robust design and functional advantages make them a preferred choice for many pipeline applications.





