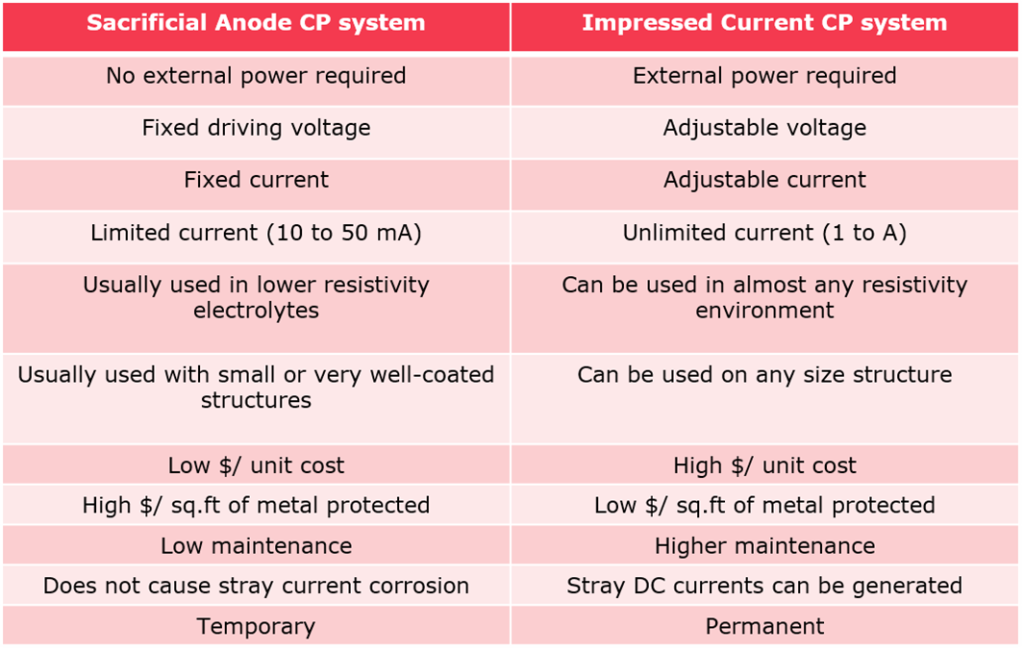
Theoratical background for corrosion mechanism
Definition
The most aggressive enemy against pipelines, or any other equipment made of metallic materials is corrosion. Corrosion happens because processed metals tend to be in unstable energy levels. Other metals with “Stable” energy levels, like gold, are nearly immune to corrosion. These metals are known as “Noble Metals”.
Corrosion Components
For corrosion to occur, four components must be present:
(1). Anode: Where electrons generated by the formation of metallic ions
(2). Cathode: Which is the reaction site for the electrons.
(3). Metallic Connector: The path that connect anode and cathode in which electrons can pass through.
(4). Electrolyte: The medium which completes the electrical circuit involves the flow of ions.
The corrosion that takes place in iron Fe when connected to more active metal, say copper, follows these reactions:
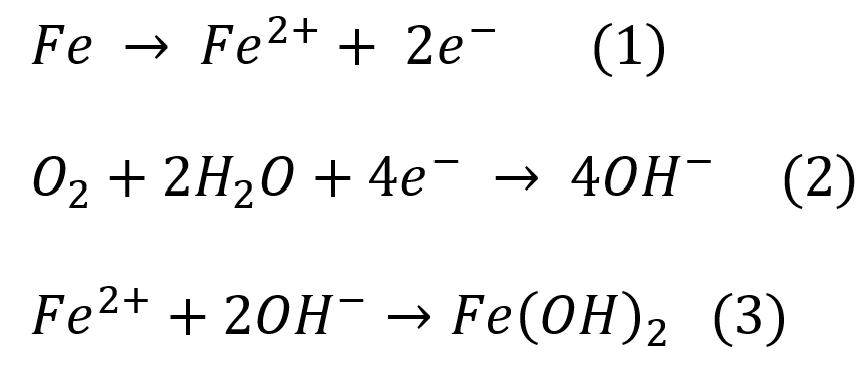
Galvanic Activity

Corrosion Types and Protection Methods
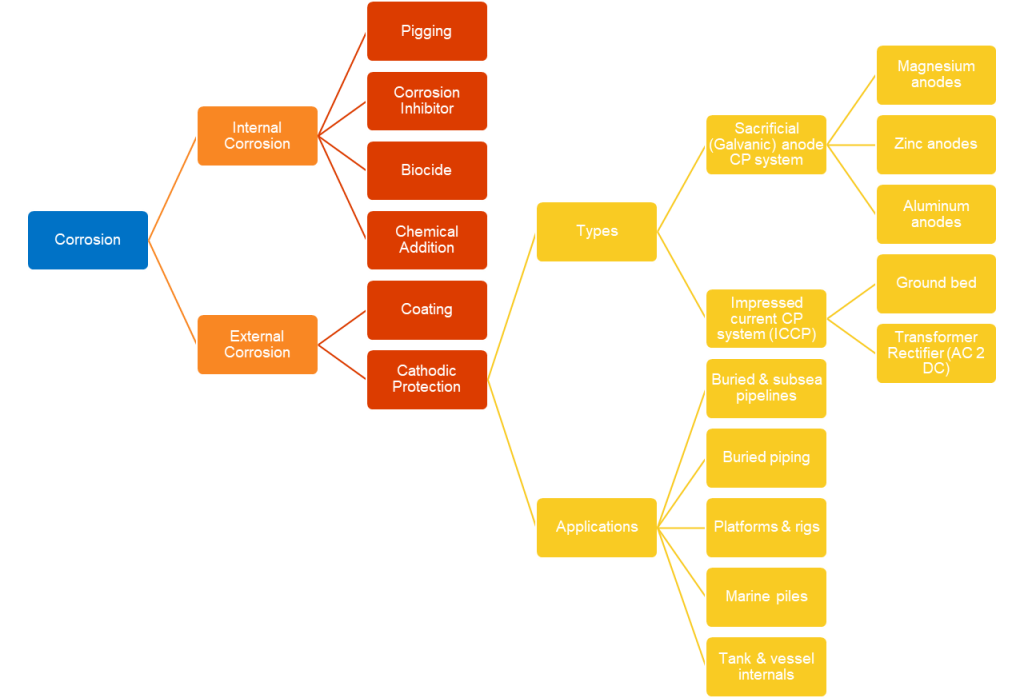
Types of Cathodic Protection
By using Cathodic Protection, we are trying to make the pipeline as cathodic as possible.