What are CS pipe grades and what is the selection criteria?
- The decision to go for CS depends mainly on economics as well as other factors such as:
- Replacement capabilities
- Maintainability
- Criticality of service
- The recommended selection process ranking where No.1 is the most favourable economically is as follow:
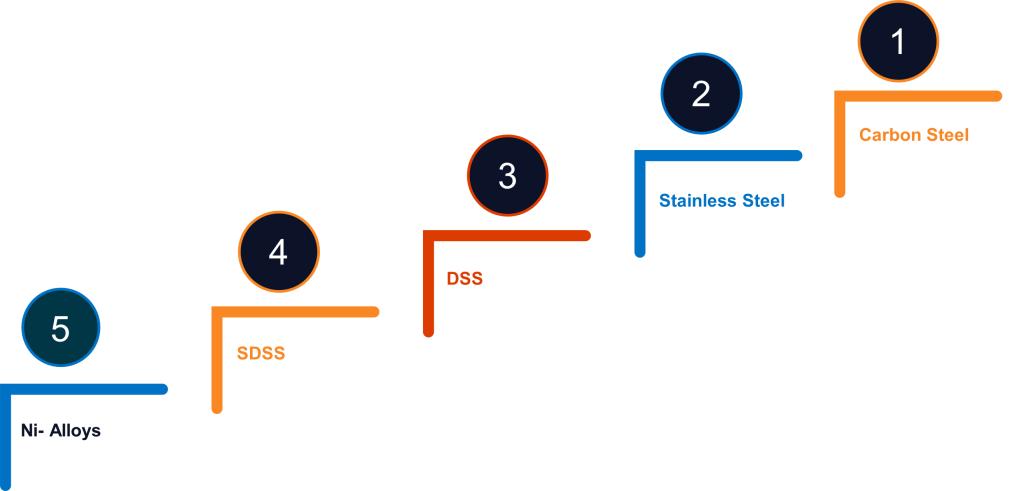
- In accordance with API 5L, we have the following CS pipe grades based on the heat treatment and the yield strength:
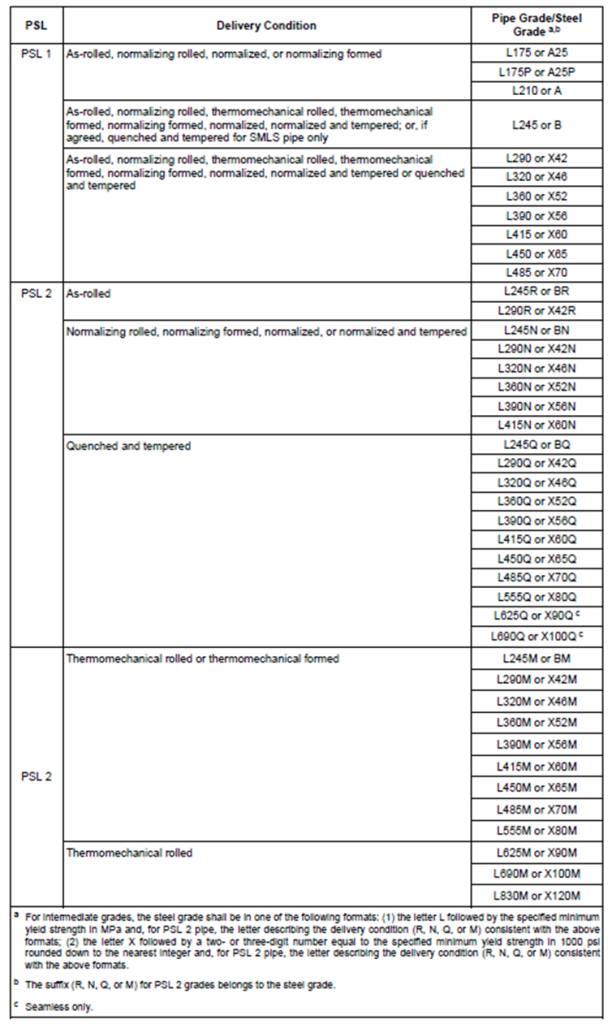
The following points highlight general practice when using CS pipes:
- CS pipelines are commonly constructed with line pipe in steel grades L290/X42 up to L450/X65 as defined in ISO 3183/ API 5L.
- Lower grades such as L245/B and higher grades may be appropriate in some cases.
- Higher grades have been encountered in the industry for higher failure probability such as hydrogen embrittlement by cathodic protection, weldability, required tensile to yield ratio.
- Use of grades L555 and above should be avoided.
- SMLS, HFW, SAW line pipes can be used for most services.
- HFW shall not be used for critical sour applications.
- D/t is limited to 75 for grades X52 and below.
- D/t is limited to 65 for grades above X52.
- Limited to a maximum wall thickness of 25 mm
- For grades higher than X65, weldability test shall be evaluated.
- For manufacturing CS, we use Submerged arc welding (SAW) and High frequency welding (HFW)
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) is used to weld line pipes together.
- API 1104 is used for the selection of the electrodes used in welding pipes together.





