What are flanges and their respective types?
Flanges are a standardized pipeline component used to join line pipes/fittings together. Pipeline flanges in good practice are constructed from the same pipeline material and with the same internal diameter. ASME B16.5 provides guidelines for flanges pressure ratings and their respective dimensions. s an engineer, you have to pay attention to the following:
- Flange Designation
- Flange designation is assigned by the vendor supplying the flanges and is structured based on the vendor’s international standards in use. A designation example is ISO 15590-3 YY, where the YY is a description of the material grade used in constructing the flange (e.g., ISO 15590-3 L290, ASTM A694 Grade F-65)
- Size and Class
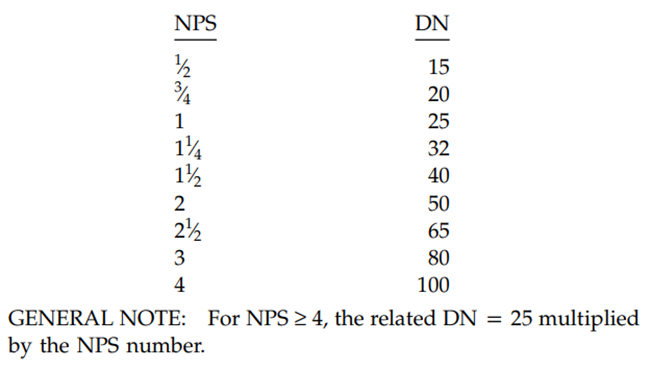
- Size is denoted by NPS which is the designation for nominal flange or flange fitting size. NPS is related to the reference nominal diameter DN mainly used in international standards. The relationship is typically as follows:
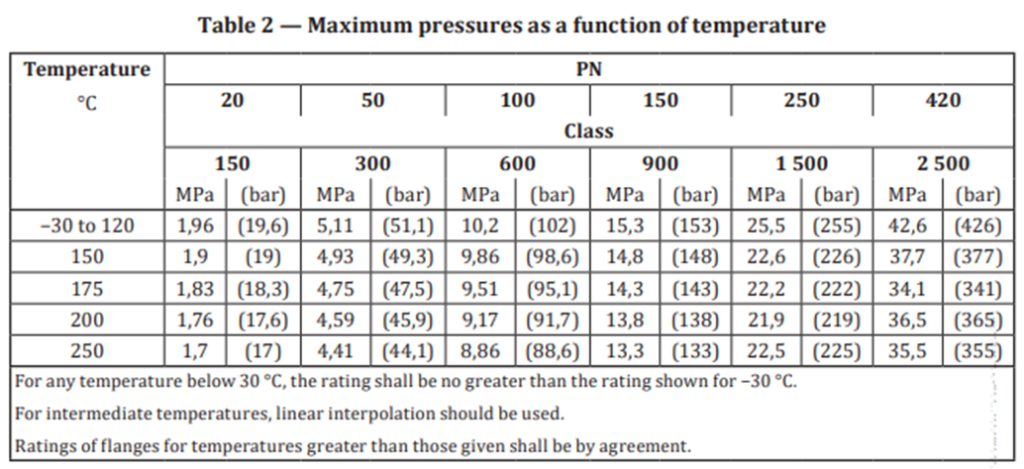
- Pressure-temperature class ratings are the maximum allowable working gage pressures at the given temperatures. For intermediate temperatures, linear interpolation is permitted. Interpolation between different class designation is not permitted.
- Material Grade
- The material grade in use in manufacturing the flange must match the line pipe’s grade.
| Requirements/ Material Option | ISO 15590-3 | A694 & MSS SP-44 | ASTM A350 & MSS SP-44 | ASTM A105N & MSS SP-44 (Class 2 or 3 with design Temp. 5 to 82 C) |
| Grades | L290 to L450 All other requirements are as per ISO 15590-3 | F42 to F65 | 1) LF2 Class 1 or Class 2 with grades L245 to L290 2) LF6 Class 1 or LF6 Class 2 /Class 3 with grades L360 and above | NormalisedAs per IOGP S-563 datasheet IC004S |
| Chemical Composition (minimum requirements) | C ≤ 0.23%, S ≤ 0.020%, P ≤ 0.025%, CE ≤ 0.43 | |||
| Impact testing | Impact testing is required for thickness ≥ 6mm for forgings. | |||
| Sour requirements | Production hardness testing shall be performed in accordance with ASTM A350 requirements. | Production hardness test as per ASTM A105 | ||
| Dimensions & Tolerances | MSS SP-44 / ASME B16.5 / ASME B16.47 Series A | |||
- Wall Thickness
- For inspection purposes, the minimum wall thickness of flanges must be the same as provided in ASME B16.5 Table 9 II – Table 12 II during the time of manufacturing. The additional metal thickness is needed to withstand installation of bolt-up assembly stresses, shapes other than circular, and stress concentrations must be determined by the manufacturer
- Flange Facing
- Flat, raised face, ring type flange.
What are flange facings?
As a rule, the flange facing must match with the gasket and bolting assembly. In practice, the smaller the contact surface area, the harder the sealing material in use is. That is because smaller contact surfaces can handle high pressures because of the formula pressure = force/ area. The primary types of flange facings are flat face, raised face, and ring type joint. There are other types which are less common such as lap joint, male and female, and tonnage and groove.
| Facing\Properties | Pressure Class | Temperature Range | Sealing Area | Sealing Face | Gasket Type |
| Flat Face – FF | 150# – 300# | Low temperature | Large | ID to OD | Soft/Non-metallic |
| Raised Face – RF | All | Low – High | Medium | ID to RF OD | Non-metallic / Semi metallic |
| Ring type joint – RTJ | > 900# | Low – High | Small | Groove in flange face | Hard / metallic |