What are the various materials used to construct line pipes used in the pipelines industry?
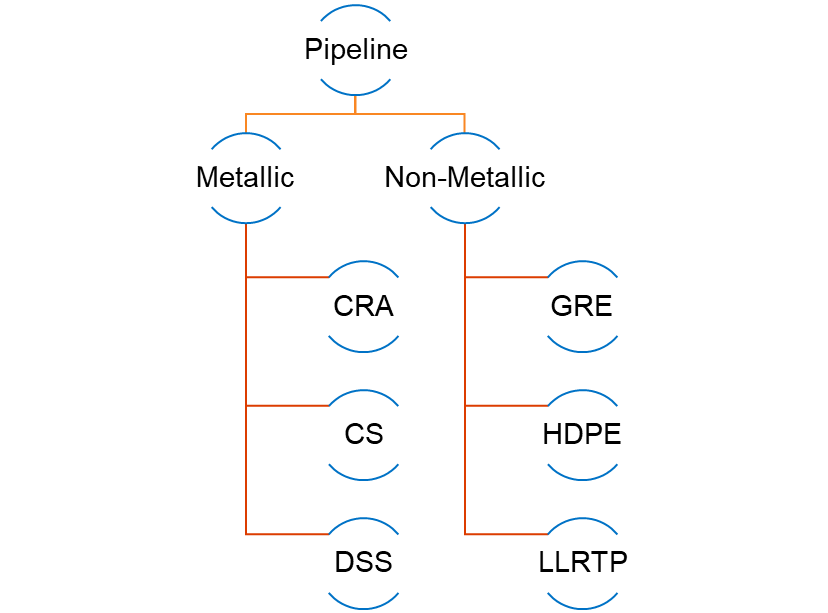
Material selection is a crucial step in any pipeline project that relies on a number of parameters such as the fluid category, service life, aboveground/burried, and the associated costs. The materials in use for pipeline projects vary from one organization to the other, but in general, the following highlights the most common types used for linepipe construction.
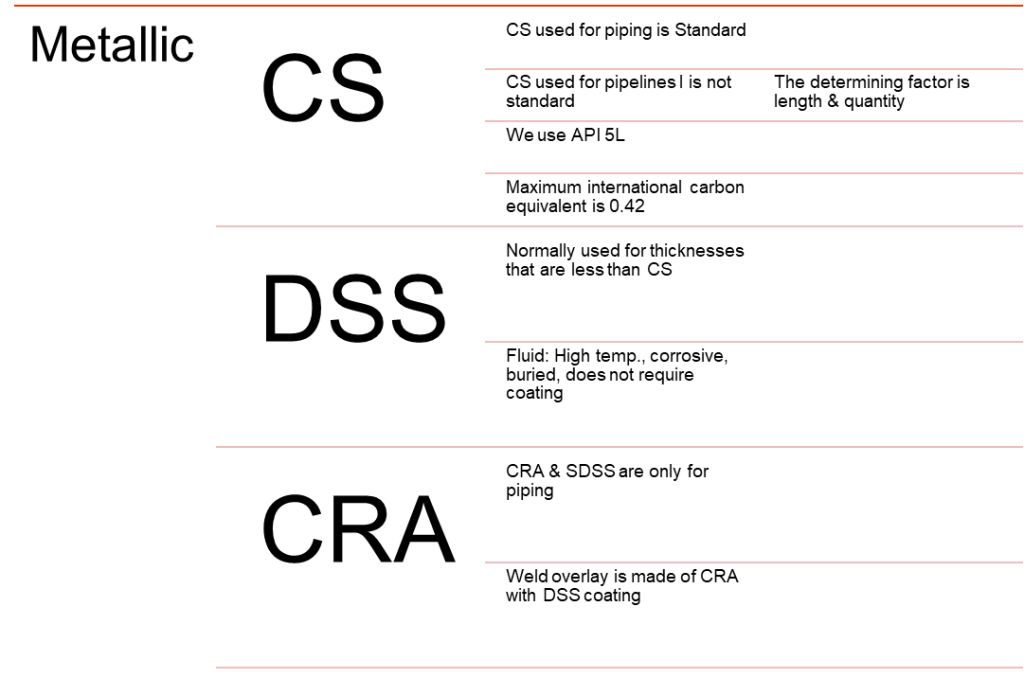
Metallic materials include Carbon Steel (CS), Corrosion Resistant Alloys (CRA), and Duplex Stainless Steel (DSS). Carbon steel used inside the facilities for piping purposes is standarized in terms of wall thickness. However, for off-plot uses, CS is not standarized and often requires customization from the manufacturers. This step mainly depends on the length/quantity needed. The followed international standards for CS linepipes are API 5L and ISO 3183-3. When choosing CS, the carbon equivalent must be investigated in terms of weldability and hardness. The following tabel highlights the most common CS grades used in pipeline projects with different namings in accordance with the relevant international standards.
| Item | Material | Grades in accordance with API 5L | Grades in accordance with ISO 3183-3 |
| Linepipe | Carbon Steel | Grade B / X42/ X46/ X52/ X60/ X65/ X70/ X80 | L245/ L290/ L360/ L415/ L450/ L485/ L555 |
The second type is DSS which is used for wall thicknesses that are less than CS (<4.6 mm). DSS is more expensive than CS and is used for transporting fluids that are corrosive and with high temperatures. Steam lines are a good example to consider the use of DSS. The last type which is CRA is restricted for piping uses.
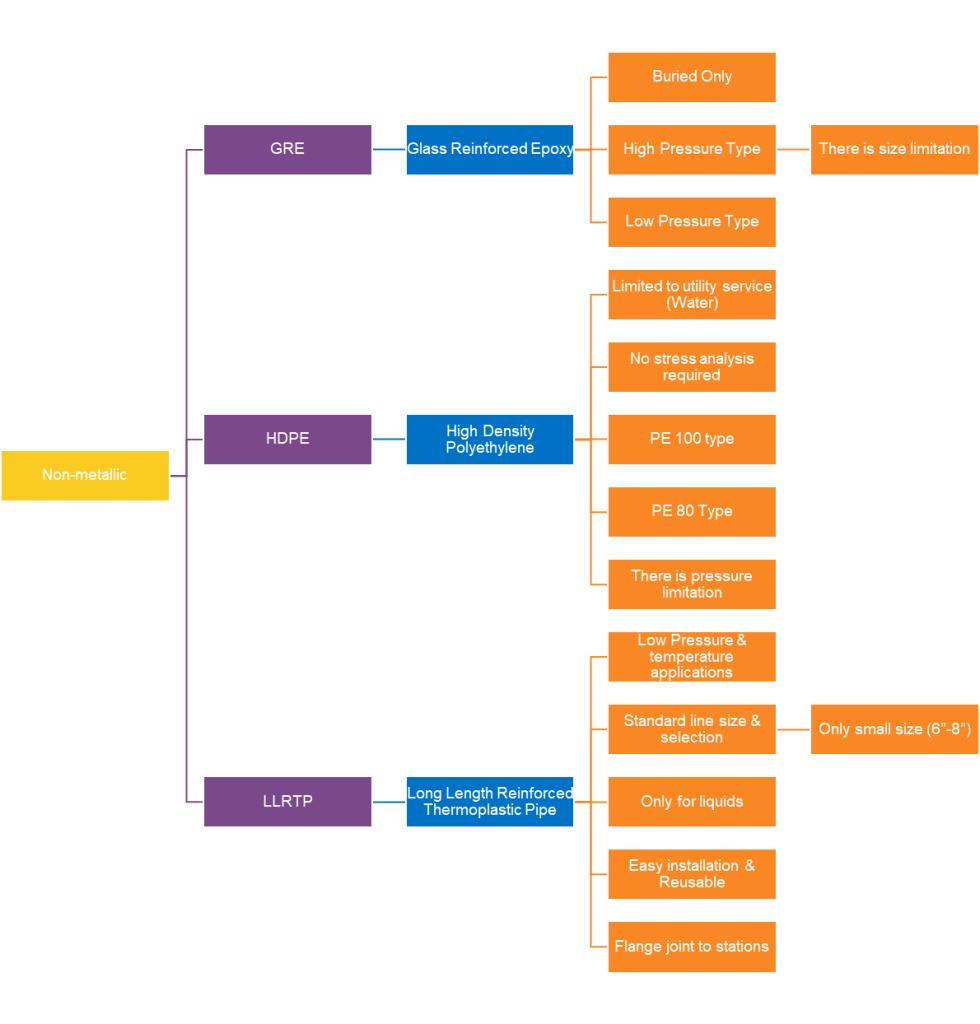
Nonmetallic materials include GRE, HDPE, and LLRTP. In first, GRE & GRP are used for transporting the same type of fluids, but the difference is the operating pressure. GRE is used for high pressure while GRP is used for low pressure applications. The main disadvantages is that GRE has a size limitation and is a costly MoC.
The second type which is HDPE is used as liner with CS host pipe to transport crude or utility fluids. PE100 type is used to transport both crude and water with a temperature less than 70 degrees Celcius. PE80 is used for transporting water only and can withstand higher temperature than PE100. The main disadvantage with PE liners is a pressure limitation.
The last type is Long Length Reinforced Thermoplastic Pipes (LLRTP). This type normally comes in with lengths of up to 500 m line pipe in a coil. It is used for pilott projects and quick installation. The associated limitations is the line size and is that it is only for transporting liquids.